Version 2025.0
General
- POLIGONSOFT documentation has been revised and added with new sections.
Mesh Generator
- Assembly based on the SALOME 9.12 platform.
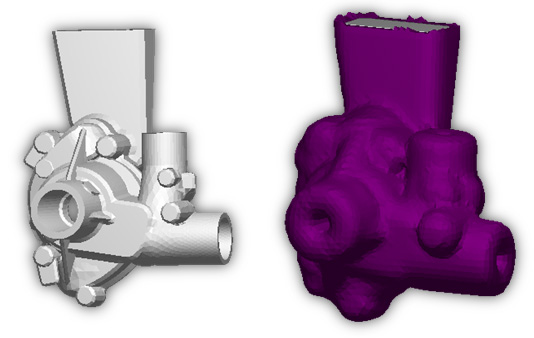
- Automatic correction and improvement of surface quality during geometry import operation has been added.
- 2D mesh correction algorithms have been refined and improved.
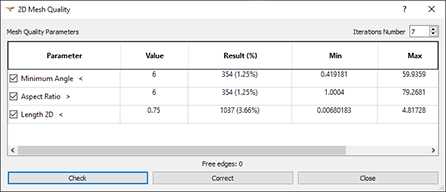
- 2D mesh checks for intersections and overlapping elements with automatic correction have been added.
Master Preprocessor
- A new tool for batch calculations has been added to the Model Tree tab (see the image below). It allows you to create a list of projects to be run. The list supports import, export, editing, sorting, and selective execution.
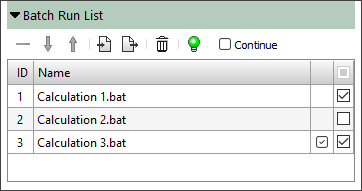
Batch Run List panel
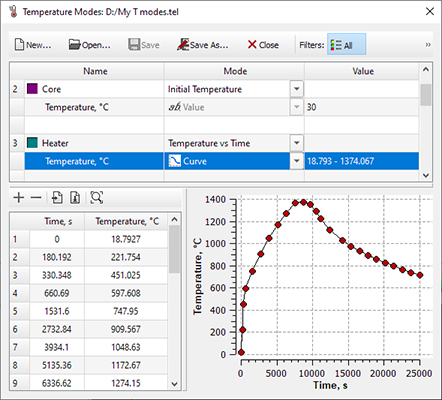
- A new Dynamic Environment editor has been added, allowing you to define the behavior of a multi-layered environment (see the image below). The legacy editor in the Alloy module is no longer used. The new editor is used in conjunction with the new Dynamic Environment tree, which has been added to the Project Overview panel. Support for legacy .air files (data import only) is retained.
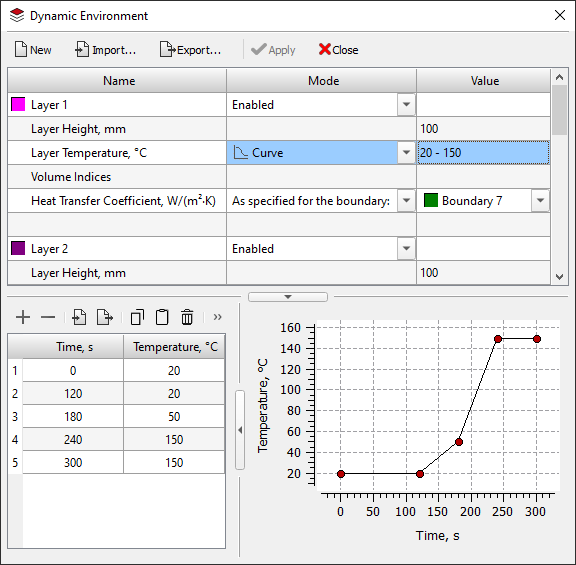
Dynamic Environment editor
- Hardenability curve and thermokinetic diagram generators for steel based on its chemical composition and other parameters have been developed and implemented (see figure below). This new tool solves the problem of inputting the initial data required for heat treatment calculations and, overall, provides valuable information needed for designing heat treatment regimes.
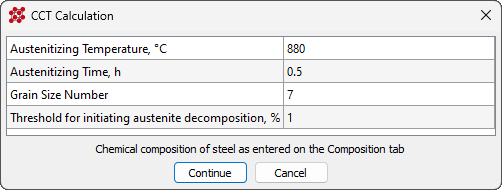
CCT diagram generator dialog
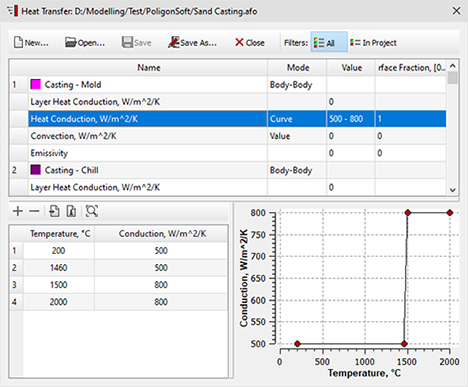
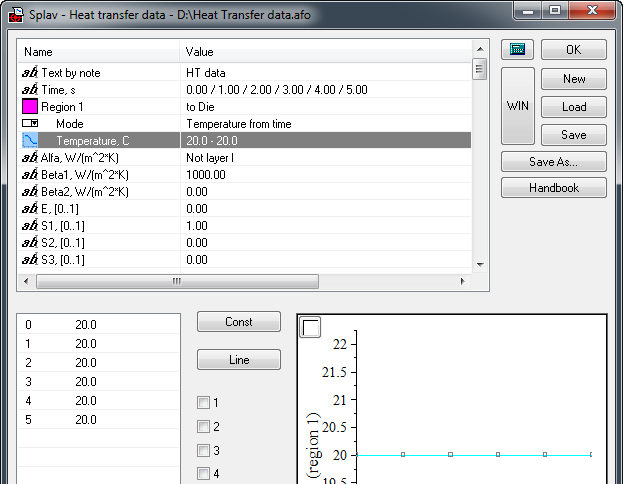
- The ability to specify heat transfer conditions on non-coincident casting and mold meshes has been added to the Heat Transfer editor. The legacy Sliding Faces editor in the Alloy module is no longer used. The Sliding Faces File line has been removed from the Solidification tab of the Start Simulation and Parameters dialog box. Support for legacy .knt files (data import only) has been retained.
- A new Gas tab has been added to the Material Properties editor (see image below). Data from this tab is used when simulating the mold's gas flow using the new model available starting with this version.
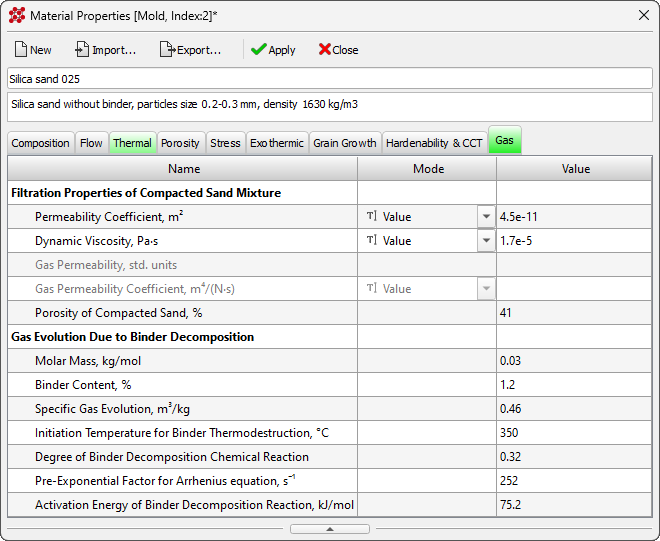
A new Gas tab
- Calculation of properties required for predicting shrinkage porosity is now available in the Material Properties editor.
- The calculation of the Hardening curve based on Young's modulus is available in the Material Properties editor on the Stress tab.
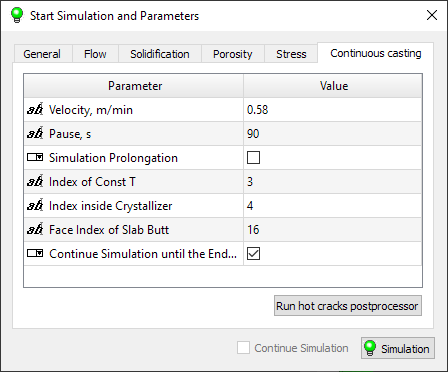
- The Create Billet and Delete Billet commands for continuous casting process simulation have been added to the Edit tab of the ribbon menu.
- A new Enable New Pipe Aalgorithm parameter has been added to the Porosity tab in the Start Simulation and Parameters dialog.
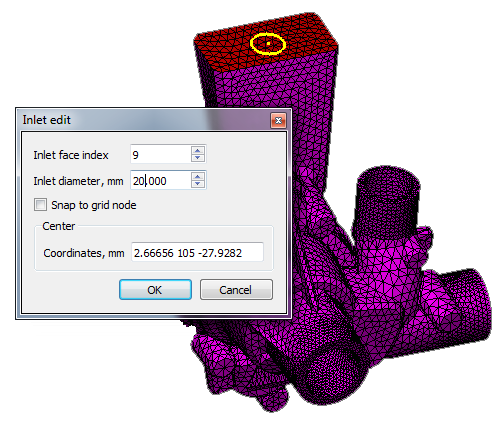
- A new Inlets parameter has been added to the Flow tab in the Start Simulation and Parameters dialog.
- A new Computation Domain parameter has been added to the Flow tab of the Start Simulation and Parameters dialog box. This parameter limits the computation domain for the flow model (Euler solver).
- A new Use Radiation File parameter has been added to the Solidification tab of the Start Simulation and Parameters dialog. This option allows you to use an existing .rad file for radiative heat transfer calculations in cases where the finite element mesh and its boundary indices have not been modified. This can significantly reduce calculation time.
- The lower limit of hardness in HRC has been expanded with the input of the hardenability curve.
- The input limits for tempering temperature have been expanded when using models based on the Spies and Just dependencies.
- A new Mold Gas tab has been added to the Start Simulation and Parameters window (see the figure below). This tab contains the parameters required to run the mold gas calculation.
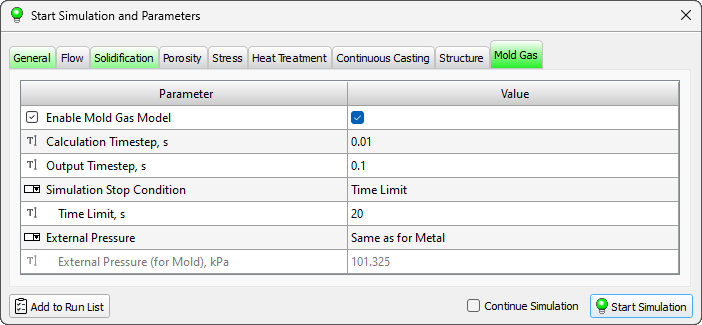
A new Mold Gas tab
- New Hardenability Curve Ajustment and CCT Diagram Ajustment parameters have been added to the Heat Treatment Model tab of the Settings window. These allow experienced users to control the model's algorithms.
- The tree structure on the Project Overview tab and all editors (Heat Transfer, Translations, Temperature Modes, etc.) have been significantly redesigned and now interact as a single tool for setting parameters and calculation conditions (see the figure below

Project Overview tab
- The Start Simulation and Parameters dialog has been significantly redesigned and improved (see the figure below). New checks and tooltips have been added for when entered parameter values are incorrect or require user attention.
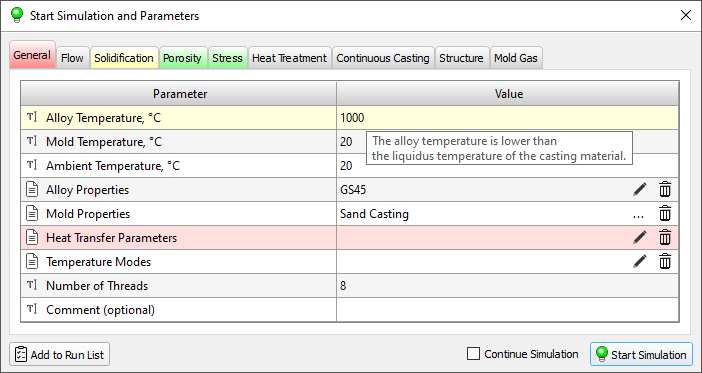
Start Simulation and Parameters dialog
- Improvements and fixes have been made to the Settings window. Specifically, resetting settings to default can be done either completely or for just the active tab.
- Improved analysis of heat treatment model parameters when running a calculation, displaying warnings to the user.
- Improvements to the display of license parameters in the About window.
- Fixed a project reading error that could occur when loading macrostructure solver parameters.
- Fixed a bug that caused partial data loss when loading projects created in previous versions.
- Fixed an error that caused the Inclosure information to be lost when saving a project. This error occurred if the Radiation parameter was not enabled on the Solidification tab in the Start Simulation and Parameters dialog.
- Fixed an issue where information in the Temperature Modes editor would not update. This occurred when creating a continuous casting billet.
- Fixed a bug where heat treatment projects from previous versions would load with default settings.
- Fixed a bug where loading heat treatment projects could cause inaccuracies in the chemical composition of steel.
- Fixed a bug where loading any projects could automatically assign Surface Nucleation conditions
- Other numerous improvements.
Databases
- The legacy editors of the Alloy module have been completely replaced with new property and boundary conditions editors. The Alloy module has been removed from the POLIGONSOFT product line.
- The materials database has been supplemented with the new material properties.
- Filtration properties and gas emission characteristics for sand molds have been added to the materials database.
Tracing Module
- Speeding up the module's operation due to improvements and optimizations when reading source data.
- Bug fixes and other improvements.
Euler Flow Solver
- It is now possible to limit the simulation area of a flow for cases where the geometric model consists not only of the casting and mold, but also of other elements, such as heaters, furnace, and so on. Such models are most often used in vacuum casting, where radiative heat exchange between the mold and equipment plays a significant role.
- Significant revision of the heat transfer model at the casting-mold and mold-mold interfaces in order to improve the accuracy of temperature field calculations.
- Improvements to the flow stop criterion to more accurately predict mold cavity filling problems due to premature metal cooling.
- Other numerous changes and fixes.
Fourier Temperature and Porosity Solver
- A new model for calculating the mold gas regime has been added to assess the tendency of castings to form associated defects.
- A new algorithm for calculating heat transfer in the shrinkage cavity region has been added. Its use can improve calculation accuracy when modeling large castings and ingots.
- Algorithms for handling noncoincident meshes have been reworked. Information is now read from the .jnl project file. Old format files with the .knt extension are no longer supported.
- Dynamic environment algorithms have been reworked. Support for separate temperature modes for each environment layer has been added. Dynamic environment information is read from the project's .jnl file. Older format files with the .air extension are no longer supported.
- Other numerous changes and fixes.
Hooke Stress Solver
- Fixed a bug that could cause the solver to crash when reading a temperature field from a .cst file.
Heat Treatment Solver
- The modified tempering models, used in conjunction with the hardenability model, now allow analysis for all practical temperature conditions.
- The algorithms for physically based models (PBM) have been improved, the permissible limits for the content of chemical elements and process parameters have been expanded and clarified, and other improvements have been introduced to increase the stability and accuracy of all available models.
Viewing Results
- Development of a prototype postprocessor integrated into the Master preprocessor has continued. This marks a new step toward creating a unified visual platform for working with projects and simulation results.
The postprocessor works in test mode and does not represent a complete solution. It can be used for informational purposes only.
- Added visualization of moving objects in accordance with the specified Translation modes.
- Added the ability to update calculation results during its execution.
- The calculation of the cross-section and isosurfaces of the casting and mold has been significantly reworked and accelerated.
- Loading of large files has been significantly accelerated.
- Fixed bugs related to displaying fields in conjunction with transparency mode.
- Fixed a bug that caused the program to crash when loading temperature fields.
- Other fixes and improvements.
Postprocessor Mirage
- The development of the obsolete module has been discontinued, it will be replaced with a new solution. In future versions, Mirage may be excluded from POLIGONSOFT.
- Bug fixes, improvements and changes related to supporting the current version of POLIGONSOFT.
Version 2024.0/2024.1
General
- Starting with version 2024.0, POLIGONSOFT has the new Guardant licensing system, which supports hardware and software license keys. The previous CodeMeter licensing system will be supported, but new license keys will not be issued.
- POLIGONSOFT documentation has been revised and added with new sections.
Mesh Generator
- Assembly based on the SALOME 9.12 platform.
- New mesh Gmsh generator is added.
- 2D mesh correction algorithms have been refined and improved.
Master Preprocessor
- The ability to specify heat fluxes at the outer boundaries of the computational domain has been added to the Heat Transfer editor (see figure below). The outdated Heat Flux editor of the Alloy module is no longer used. The Heat Flux File line has been removed from the Solidification tab in the Start Simulation and Parameters window. Old format files with the qgr extension can be imported into the Heat Transfer editor.
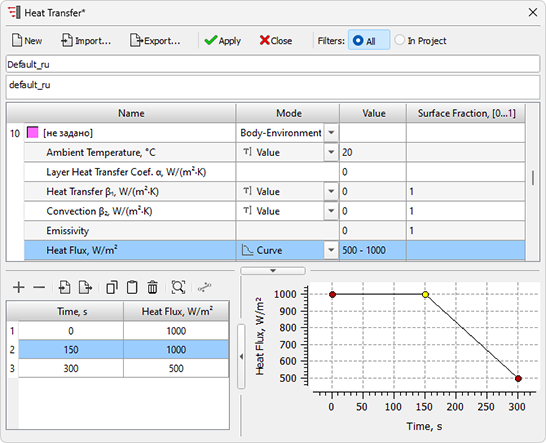
Heat Transfer editor with the ability to set heat flux
- A new Translation editor has been added for the ability to specify the movement of bodies in the computational domain (see the figure below). The legacy Movement Mods editor of the Alloy module is no longer used. The new editor is used in conjunction with the new Translations Tree that has been added to the Project Overview panel. Support for legacy movement files with the mve extension has been retained (data import only).
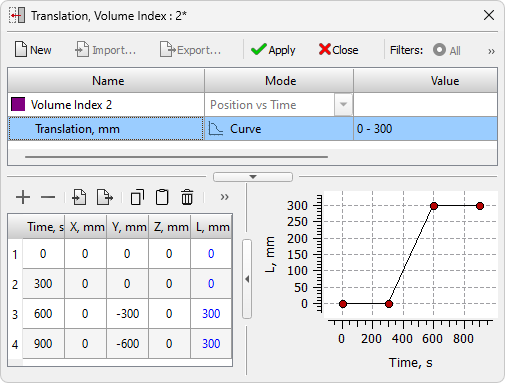
Translation editor
- A new Hardenability & CCT tab has been added to the Material Properties editor (see the figure below). This tab is used to model heat treatment processes in the updated Heat Treatment solver.
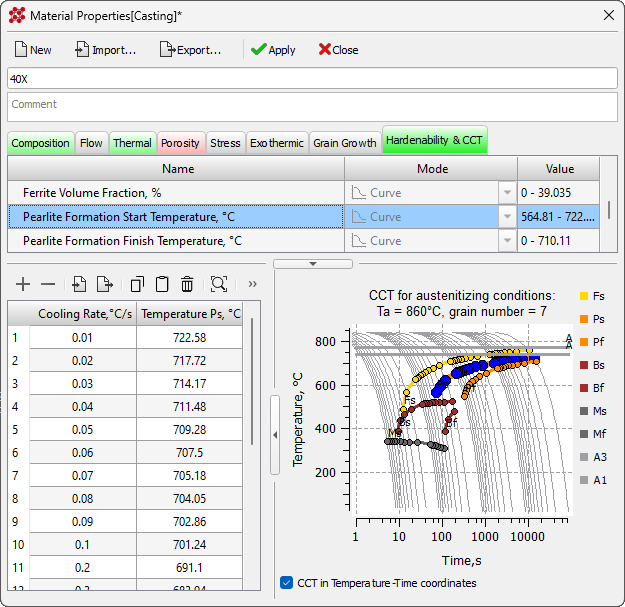
Hardenability & CCT tab in Material Properties editor
- A new Surface Nucleation editor (see the figure below) and a tree of the same name on the Project Overview tab have been added for creating and editing parameters for the nucleation of different types of structures on casting-mold surfaces. The editor data is used in the updated Macrostructure solver.
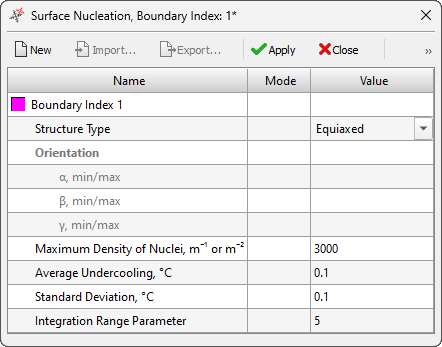
Surface Nucleation editor
- A new Structure Inheritance editor (see the figure below) and a tree of the same name on the Project Overview tab have been added for creating and editing parameters for the inheritance of different types of structures on surfaces of the computational domain. The editor data is used in the updated Macrostructure solver.
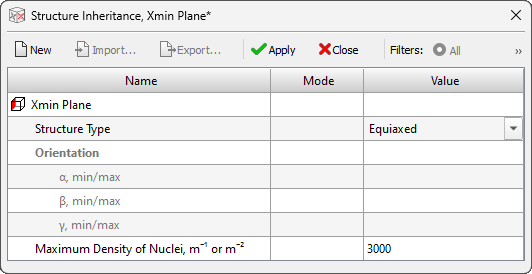
Structure Inheritance editor
- The ribbon menu has been made the default interface when installing POLIGONSOFT. The classic interface based on the menu bar and toolbars is still available. The ability to select the size of the buttons on the toolbars has been added to the classic interface.
- Added new display modes Casting Transparency and Mold Transparency
- The design and functionality of the Model Tree has been redesigned and significantly improved.
- The Detuch Index option has been significantly improved and added to the Model Tree. The option is used to set heat transfer at casting-casting or mold-mold boundaries. Previously, this required additional use of the Sliding Boundaries editor. Now, when using coincident meshes, this is not necessary.
- The Empty for Stress option control has been added to the Model Tree. The option is used to exclude some areas of the mold from the stress calculation.
- The Volume Parameters dialog have been redesigned and improved.
- Functionality of the Measure tool has been improved. Added a button to reset measurement points.
- The Grain Growth model parameters input in the Material Properties editor has been improved.
- The Continue Simulation option on the Continuous Casting tab in the Start Simulation and Parameters window has been removed because it is no longer needed.
- An option that automatically selects a color for the Section Plane depending on the selected background color has been added.
- The Structure tab in the Start Simulation and Parameters window has been redesigned to work with new Macrostructure solver models.
- The functionality of the Stress tab in the Start Simulation and Parameters window has been improved. In particular, the calculation launch is handled more correctly if the geometry does not contain a mold.
- The error that caused the casting material to be replaced when assigning volumes of the Empty type has been fixed.
- A bug that caused the list of temperature modes to be displayed incorrectly has been fixed.
- A bug that made it impossible to set negative values (for example, “-1”) for the Mold Removal Temperature and Gating System Removal Temperature parameters has been fixed. Negative values for these parameters indicate that the temperature field calculated in the last step of the thermal calculation should be used.
- A bug that could cause the program to crash when deleting a volume has been fixed.
- A bug that caused the program to crash when selecting boundaries using the Use Section filter has been fixed.
- A bug that caused a crash when dragging a g3d file from Windows Explorer into the program has been fixed.
- A bug that caused data loss when exporting heat transfer parameters has been fixed.
- A bug that caused a solidification calculation error when there was no mold has been fixed.
- Other numerous improvements.
Databases
- The outdated editors of the Alloy module are replaced by new editors of properties and boundary conditions. The development of the module has been discontinued, in future versions it may be excluded from POLIGONSOFT.
- The outdated Heat Flux editor of the Alloy module is no longer used.
- The legacy Movement Mods editor of the Alloy module is no longer used.
- The materials database has been supplemented with the new material properties.
- The steel properties database has been supplemented with data on hardenability and CCT diagrams of austenite decomposition.
Tracing Module
- Support for movement files of the old format with the mve extension has been discontinued. Reading information about object translations is performed from a project file with the jnl extension.
- Bug fixes and other improvements.
Euler Flow Solver
- The computing speed has increased by up to 30% compared to the previous version due to optimization of computing procedures.
- The ability to continue calculations with changes in the inlets and outlets operation has been added.
- Hydrostatic pressure (in atmospheres) output added to universal format file with u3d extension.
- The temperature field interpolation procedure has been redesigned to obtain a more stable and accurate result.
- The recording of the dump status file is synchronized with the recording of the result files.
- A bug that made it impossible to calculate HPDC process if the flow velocity was not in the X or Z direction has been fixed.
- A bug with incorrect initialization of the temperature mode for internal (meltable) chills has been fixed.
- The error that made it impossible to start a calculation in the absence of a boundary with index 17 has been fixed.
- A bug that in some cases caused the melt temperature at the inlet to increase has been fixed.
- Other numerous changes and fixes.
Fourier Temperature and Porosity Solver
- Operations with heat flux specified at external boundaries have been improved. Now information about heat flux is read from the jnl project file. The old file format with the qgr extension is no longer supported.
- Algorithms for working with translations have been redesigned. Now information is read from the jnl project file. The old file format with the mve extension is no longer supported.
- Procedures related to the processing of moving objects during radiation heat transfer have been improved and redesigned.
- Algorithms for the "cast-to-cast" and "mold-to-mold" interface types processing have been redesigned. Now, to define heat transfer between coincident meshes of the same type, you no longer need to use a .knt Sliding Faces file.
- The algorithms of the continuous casting model have been significantly revised and improved. This has increased the accuracy of calculating the temperature fields in the mold and the moving slab. The procedure for selecting the calculation step and the saving step has been changed. The calculation step can now be set by the user. The saving step set by the user is taken into account when calculating the pause before the start of the slab movement. Restoring the calculation of continuous casting now follows the general rules for all thermal calculations.
- A bug that could cause calculations to stop when too many thermal nodes were generated has been fixed.
- Other numerous changes and fixes.
Hooke Stress Solver
- The displacement field in the .nds file is now recorded in millimeters.
- Creating the files *_gap.u3d and *_gap_mm.u3d (the gap size between the casting and the mold) is blocked when calculating stresses after removing the mold and elements of the gating-feeding system.
Macrostructure Solver
- A new version of the solver for calculating the macrostructure has been added to POLIGONSOFT, it replaces the previous version Structure-2D.
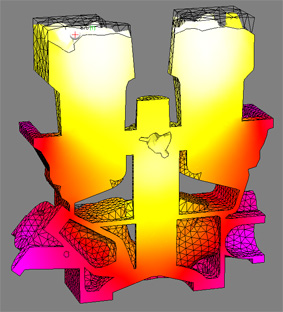
- The solver can calculate the structure both in a given section (2D problem) and in a given three-dimensional region (3D problem) (see the figure below).
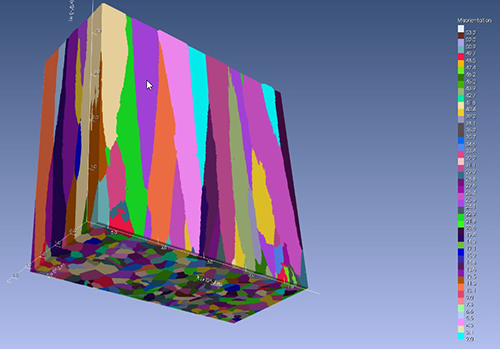
Example of modeling the nucleation and growth
of a directed structure (3D problem)
- The ability to specify different parameters for the structure nucleation at casting-mold type boundaries using different boundary indices has been added.
- When assigning the nucleation parameters, you can select the structure type (equiaxed, texture, or single crystal) and set its orientation ranges. This allows you to simulate contact with the seed.
- The ability to set parameters for inheriting the structure at the boundaries of the calculation area where there are no boundaries of the casting-mold type has been added.
- Numerous other improvements.
Heat Treatment Solver
- The Heat Treatment solver is integrated into the Fourier solver and works in coupling mode with it.
- The number of models for heat treatment processes analysis for steels with austenitic transformation has been expanded, and new models have been added:
- model using data of the steel hardenability;
- a generalized model based on the Scheil-Can additivity rule, Johnson-Mehl-Avrami-Kolmogorov (JMAK), Kostinen-Marburger, and Zener-Hillert equations.
- The number of models for analyzing steel tempering processes has been expanded for use in combination with all available austenite decomposition models. The Just and Spies tempering models have been added.
- An algorithm for automatically controlling the calculation step has been added. In this case, the value of the Calculation Timestep parameter determines the maximum calculation timestep, which can be automatically changed as the calculation is performed to ensure that the result is obtained with sufficient accuracy.
- Numerous improvements to the stability of the models have been introduced, algorithms have been improved, and the limits of the content of elements of permissible chemical compositions of steels have been expanded.
- Correction of non-critical errors in the Creusot-Loire model.
Viewing Results
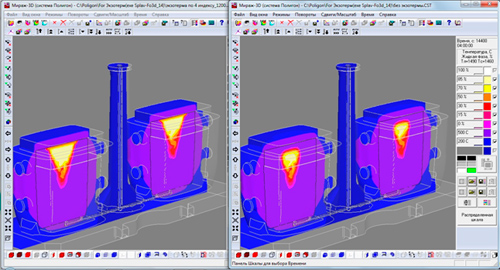
- The first prototype of a postprocessor integrated into the Master preprocessor is presented. This is the first step towards creating a single graphical platform for working with the project and simulation results (see the figure below).
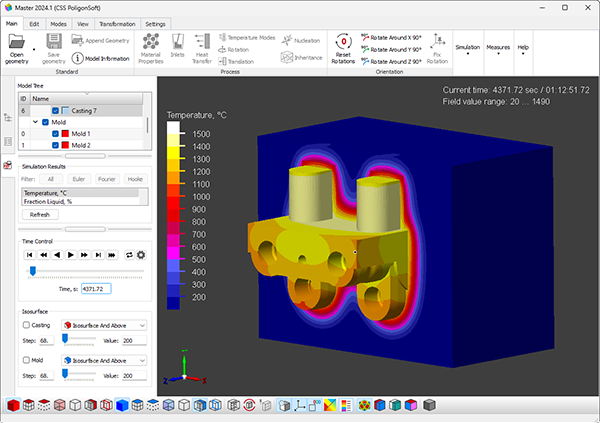
Viewer on the platform of the Master module
- Launch the postprocessor using the Open Legacy Results command on the Main tab of the ribbon menu or from the File menu.
The postprocessor works in test mode and does not represent a complete solution. It can be used for informational purposes only.
- Loads CST+MLD files and visualizes temperature fields and liquid phase fractions separately.
- All main visualization modes for casting and mold bodies are available: surfaces, sections, isosurfaces, etc.
- Extended and customizable palette containing up to 15 colors. Separate customizable scales for each field.
- Setting markers to control the value of fields at any point in the geometry.
- The Measure tool for measuring distances and dimensions.
Postprocessor Mirage
- The development of the obsolete module has been discontinued, it will be replaced with a new solution. In future versions, Mirage may be excluded from POLIGONSOFT.
- Bug fixes, improvements and changes related to supporting the current version of POLIGONSOFT.
Version 2023.0/2023.1
General
- The POLIGONSOFT documentation has been revised and updated with new sections.
- The practical guide for using POLIGONSOFT has been updated and added with a new section. It is located in the Tutorial folder.
- A new Structure2D solver has been added to POLIGONSOFT.
Mesh Generator
- Assembly based on the SALOME 9.9 platform.
- Algorithms for checking and correcting a 2D mesh have been redesigned and improved. This made it possible to significantly improve the quality of the 2D and 3D meshes.
Master Preprocessor
- A new experimental ribbon interface is available (see figure below). The classic interface based on the menu bar and toolbars is still the main one. Switching to the ribbon is possible in the module settings.
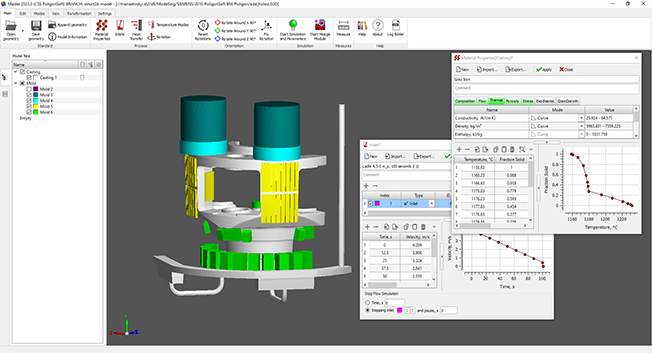
New ribbon interface of the Master module
- The Material Properties editor is now used to edit the mold material properties. The deprecated Mold Material Properties editor of the Alloy module is no longer used. The ability to load projects created in previous versions and using the bdf mold material properties file has been retained. Mold materials are now stored in pmat files, mold material sets are stored in the new pmms file type (replacing the obsolete bdf files).
- A new Project Overview tab has been added to the left panel of the module (see figure below). The tab will contain information about the current project: a list of materials, boundaries, modes and conditions. Now the Materials tree has been added to the tab, which contains information about all the materials used in the project.
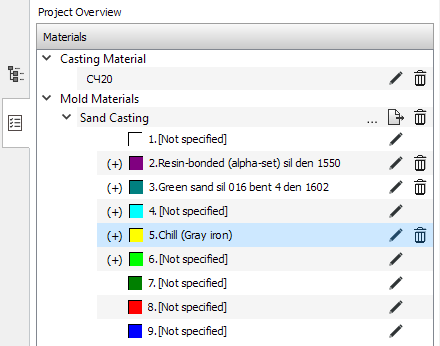
Project Overview tab
- Environment - a body that defines the area of radiative heat transfer calculation is now set in the Volume Parameters dialog or in the Model Tree tab. The information contained in the mve file is ignored.
- New Show, Hide, and Invert commands have been added to the model tree context menu to control the visibility of individual volumes and their groups.
- The new temperature mode “Temperature vs. Time with Cutoff” has replaced the outdated Exothermic Sleeve mode due to the introduction of a new model for exothermic materials. The mode is switched off if the process time exceeds the time of the last point of the temperature-time curve.
- Information about available licenses is added in the About window.
- A new Exothermic tab has been added to the Material Properties editor (see figure below). The data in this tab is used for exothermic materials simulation of the "mold" type according to the new model, which is available starting from this version.
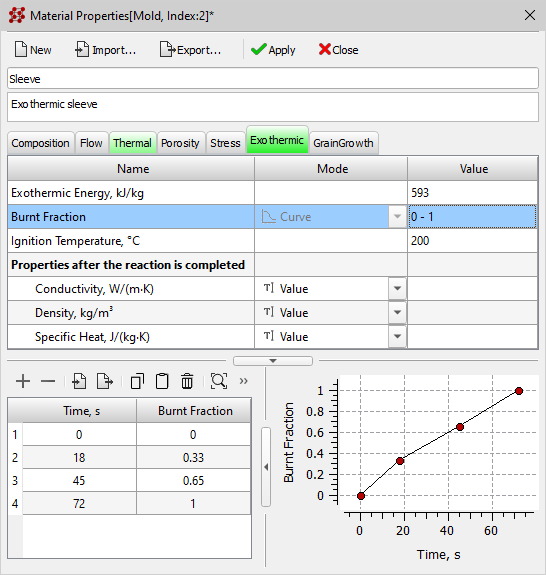
New Exothermic tab in the Material Properties editor
- A new Grain Growth tab has been added to the Material Properties editor (see figure below). The data in this tab is used by the new Structure2D macrostructure solver, which is available starting from this version.
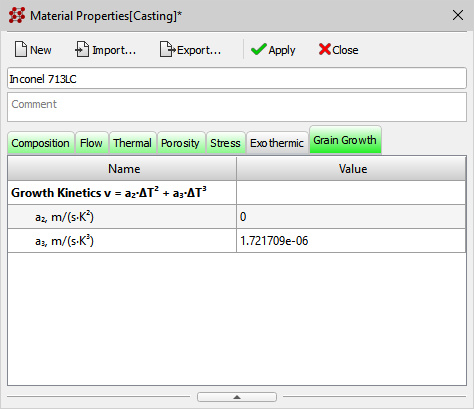
New Grain Growth tab in the Material Properties editor
- A new Structure tab has been added in the Start Simulation and Parameters window (see the figure below). The data in this tab is used by the new Structure2D macrostructure solver, which is available starting from this version.
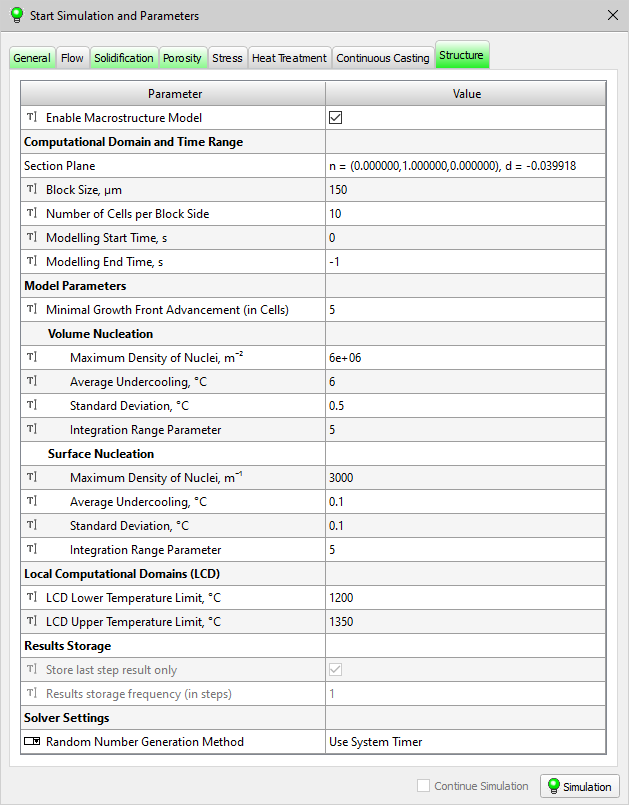
New Structure tab in the Start Simulation and Parameters window
- New parameters are available on the Heat Treatment tab in the Start Simulation and Parameters window for the new tempering model that is available from this release.
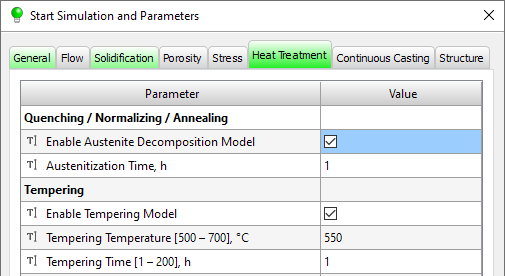
Heat Treatment tab in the Start Simulation and Parameters window
- A new Mold Stress Properties Volume Index parameter has been added to the Stress tab in the Start Simulation and Parameters window. The parameter indicates what mold stress properties will be used when modeling the contact interaction between casting and a linear-elastic or elastic-plastic mold.
- The rotation parameters used in centrifugal casting are recorded in the jnl project data file. The rot file is no longer used, but compatibility with previous versions where such a file was created is maintained.
- A parameter that disables recording dump state files has been added to the module settings.
- The range of possible values for the Secondary Dendrite Arm Spacing parameter used in new porosity model has been expanded.
- Improved checks in the Material Properties editor for the sufficiency and necessity of the entered data to start the calculation.
- Checks of solver parameters in the Start Simulation and Parameters window are improved.
- Fixed incorrect behavior in editors when changing the parameter set name.
- Bug that caused the flow solver stop parameters to reset when approach parameters were changed was fixed.
- An error in reading the new porosity model parameter Surface Tension Coefficient when opening projects of older versions was fixed.
- A bug in the bat batch file entry that caused an error when starting the calculation was fixed.
- Other numerous UI changes and fixes.
Databases
- The outdated editors of the Alloy module are replaced by new editors of properties and boundary conditions. The development of the module has been discontinued, in future versions it may be excluded from POLIGONSOFT.
- The deprecated Mlod Material Properties editor of the Alloy module is no longer used.
- The cast alloy materials database has been completely updated and expanded.
- The mold materials database has been completely redesigned, updated and included in the general POLIGONSOFT materials database. All mold materials are now stored in separate pmat files.
- Material database is supplemented with the properties of exothermic materials.
- Mold material sets used as templates can be exported to pmms files (analogous to the obsolete bdf file).
- Updated and redesigned process templates.
Tracing Module
- The mve file is not required for the module if the movement of the model bodies is not specified by the case conditions.
- Errors that occurred when processing very large meshes are fixed.
Euler Flow Solver
- The flow model has been significantly revised and improved (see the figure below) Problems with the reproducibility and convergence of the calculation results have been solved, c. including in multithreaded calculations.
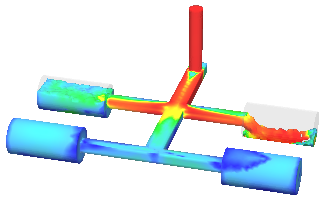 |
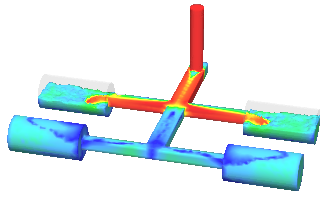 |
a) |
b) |
Improving the flow model: a) version 2022; b) version 2023
- The counting speed has been increased up to 5 times compared to the 2022 version due to the optimization of the program code and algorithms.
- The accuracy of solving the heat conduction problem has been improved, including by improving the procedure for choosing a time step.
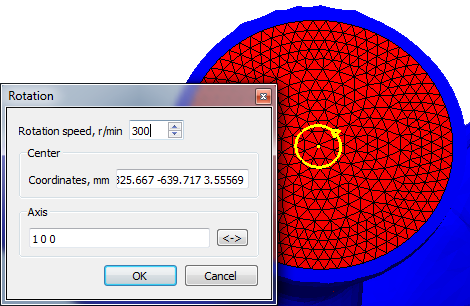
- The rotation parameters used in centrifugal casting are read by the solver from the jnl project file. The rotation file rot is no longer used.
- Bug that led to loss of reproducibility of results during repeated calculations was fixed.
- Bug that led to mismatch of results when calculating in one and several threads was fixed.
- Other numerous changes and fixes.
Fourier Temperature and Porosity Solver
- The procedure for calculating heat fluxes in radiative heat transfer has been revised. The calculation speed is increased due to the use of multi-threaded calculations.
- When calculating radiative heat transfer, the displacement file mve is not required. Information about the dimensions of the calculation area is stored in the jnl project file. The mve file is only used to get information about moving objects.
- A new model of exothermic mold materials has been implemented. The new model takes into account the heat release and transformation of the material structure as the thermite reaction proceeds.
- The rotation parameters used in centrifugal casting are read by the solver from the given jnl project file. The rotation file rot is no longer used.
- Free disk space check before writing files was added.
- A minor inaccuracy in the calculation of the temperature field has been eliminated.
- Error in calculating radiative heat transfer for models that do not contain bodies of the "casting" type was fixed.
- A bug has been fixed that could lead to incorrect search for contact nodes on the casting-mold boundary.
- Fixed bug in reading density temperature curve from alloy properties. In rare cases, the calculation did not start.
- Fixed a bug that occurred when reading incorrect temperature conditions.
- Fixed error in writing log file when restoring calculation.
- Other numerous changes and fixes.
Hooke Stress Solver
- The improvement of some solver procedures made it possible to increase the calculation speed up to 80%, depending on the number of elements and the mesh topology.
- The new parameter tells the solver what data to use to calculate the stresses in the mold.
- Bug that did not allow starting the calculation in the root directory was fixed.
- Other numerous changes and fixes.
Structure2D Solver
- A new macrostructure solver has been added to POLIGONSOFT (see figure below).
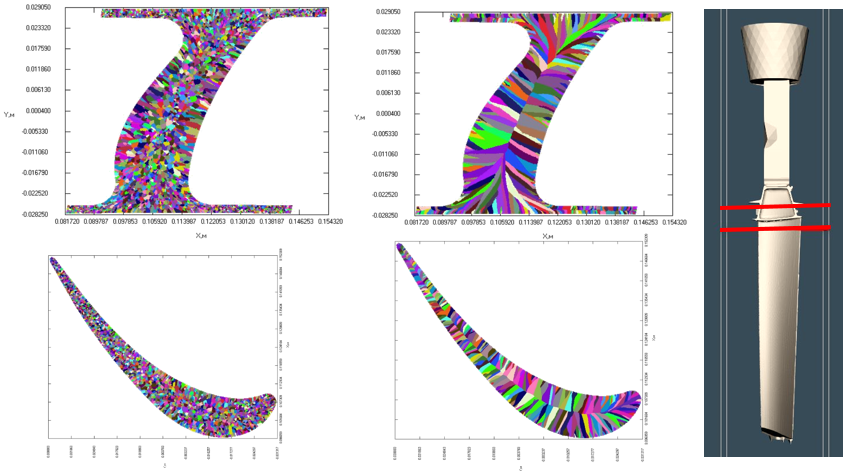
Macrostructure in the section of the blade obtained under different cooling conditions
- The solver works with a non-stationary temperature field calculated in the Fourier solver.
- The calculation of the macrostructure is carried out in the selected section of the casting.
- The parameters required to run the solver are set on the Structure tab in the Start Simulation and Parameters window and on the Grain Growth tab in the Material Properties editor.
- To view the results, a special postprocessor is used as part of POLIGONSOFT.
Heat Treatment Solver
- The basic model is supplemented with statistical models for calculating the yield strength and elongation.
- The solver is supplemented with a hardened steel tempering model. The results of the calculation will be the fields of tensile strength, yield strength, Vickers hardness and relative elongation.
- Other changes and fixes to improve the stability of the solver and the accuracy of the calculation result.
Postprocessor Mirage
- The development of the obsolete module has been discontinued, it will be replaced with a new solution. In future versions, Mirage may be excluded from POLIGONSOFT.
- Bug fixes and minor improvements.
Version 2022.0
General
- The POLIGONSOFT documentation has been revised and updated with new sections.
- The practical guide for using POLIGONSOFT has been revised and updated. It is located in the Tutorial folder.
- The new Heat Treatment solver has been added to POLIGONSOFT.
Mesh Generator
- Assembly based on the SALOME 9.7 platform.
- Automatic creation of groups of elements by geometry.
- Algorithms for checking and correcting a 2D mesh have been redesigned and improved. This made it possible to significantly improve the quality of the 2D and 3D meshes.
- Saving mesh files in med 4.1 format. Such files cannot be opened in previous versions of POLIGONSOFT. It remains possible to use previous versions of med.
- Fixed an error that occurred when re-writing the hdf file.
Preprocessor Master
- The new Extrude Mesh tool lets you quickly create new volumes from selected areas of outer boundaries. In this way, you can quickly create simple elements such as covers, insulation, chill-plates, etc.
- The new Copy/Move tool allows you to move or copy selected model bodies in a given direction (see the figure below).
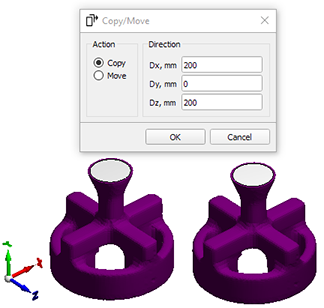
Copy/Move Tool
- The new Measure tool allows you to measure the distance between two given points (see the figure below).
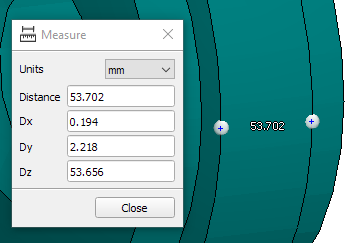
Measure Tool
- The new Material Properties editor replaces the traditional Alloy Thermal Properties, Alloy Shrinkage Properties, and Alloy Mechanical Properties editors (see figure below). The new editor provides access to all the characteristics of the material and significantly expands their list, compared to the old editors. The material properties are written to a new pmat file format, but .bd, .fil, and .bdd files can still be imported.
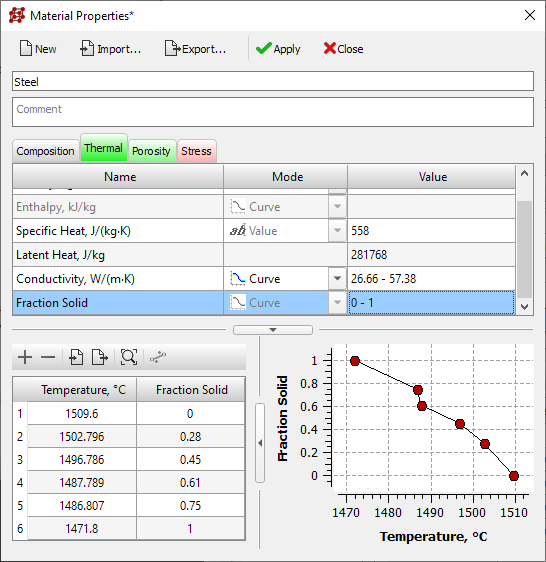
Material Properties Editor
- The new Line feature has been added to all new data editors. The function creates a linear section of the curve between two selected points (see figure below).
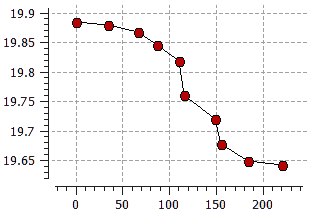 |
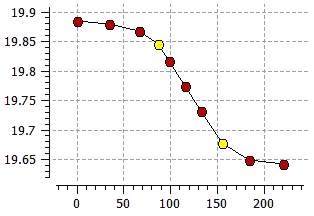 |
Initial curve |
Curve with linear section |
Example of creating a linear section of a curve
- A new Process toolbar has been added for quick access to the materials, inlets and boundary conditions editors (see the figure below).

Process Toolbar
- Buttons have been added to the Modes toolbar that enable the display of casting and mold edges.
- A quick object search mode has been added to the Model Tree. When you select a model object, the rest become transparent (see the figure below).

Transparency mode for inactive objects
- The Inlets editor has been significantly redesigned (see the figure below). Added the ability to load and edit inlets with speed profiles. The database of velocity profiles for ladles (bdv files) has been overwritten in the new format; now each file stores information about the number of inlets, their diameter, operation logic and melt velocity.
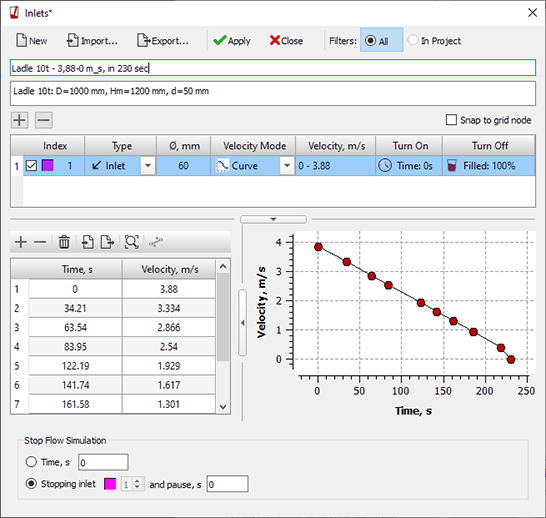
Inlets Editor
- The design of the Start Simulation and Parameters window has been updated. Added checks for the presence of parameters required to run each solver and interactive notification of the user about errors.
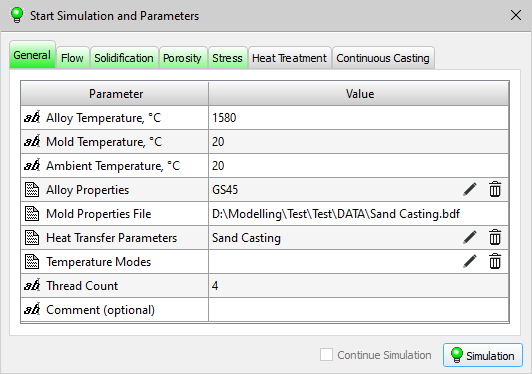
Start Simulation and Parameters dialog
- A new Only visible option has been added to the Select Boundaries tool to select the boundaries of a given index only on those bodies that are displayed in the graphics area of the module.
- The logic of working with the boundary and initial conditions of the calculation has been significantly revised and improved. Increased transparency of operations and safety of project data.
- The use of multi-threaded processing during the boundary selection operation made it possible to significantly increase performance when working with large models.
- The algorithm for restart of interrupted calculation has been improved.
- A new Heat Treatment tab has been added to the Start Simulation and Parameters window. The tab contains the parameters required to run the heat treatment solver.
- The parameters that specify the properties of the cast alloy are excluded from the Porosity and Stress tabs in the Start Simulation and Parameters window.
- The new porosity model parameters are now set on the Porosity tab in the Material Properties editor. The ModelPar.dat file is no longer used.
- The Inlet Velocity File parameter is removed from the table of calculation parameters. Melt velocities are now set in the Inlets editor.
- Parameters for calculating hot cracks during continuous casting have been added to the Continuous Casting tab in the Start Simulation and Parameters window.
- Bug that caused Surface Angle parameter to be incorrectly memorized was fixed.
- Other numerous UI changes and fixes.
Databases
- The outdated editors of the Alloy module are replaced by new editors of properties and boundary conditions. The development of the module has been discontinued, in future versions it may be removed from POLIGONSOFT.
- Old Alloy Thermal Properties, Alloy Shrinkage Properties, Alloy Mechanical Properties and Inlet Velocities editors are no longer used and are excluded from POLIGONSOFT.
- Cast alloys database in a new format for use with the new editor of material properties. Properties files in the old format are temporarily retained.
- The Inlets database in a new format.
- New cast alloy materials added to the database.
- Updated and reworked the database of mold materials.
- Casting templates updated and revised.
- Fixed data entry error in the Dynamic Environment editor.
Tracing Module
- Numerous improvements and fixes.
Euler Solver
- Module algorithms have been changed and redesigned to work with material properties in a new format. It is possible to calculate temperature fields using the enthalpy of the alloy.
- Module algorithms have been changed and redesigned to work with new inlets.
- Restrictions on the use of the number of points in the curves of material properties and flow velocities have been removed.
- The error that led to the wrong direction of rotation of the mold during centrifugal casting has been fixed.
Fourier Temperature and Porosity Solver
- Module algorithms have been changed and redesigned to work with material properties in a new format. It is possible to calculate temperature fields using the enthalpy of the alloy.
- Restrictions on the use of the number of points in material property curves have been removed.
- The algorithms of the module associated with the calculation of radiation heat transfer and the movement of model bodies have been significantly revised and improved.
- The procedure for setting the initial calculation time has been improved.
- Changed the frequency of recording the status file. Now the state file is written with a step equal to the step of saving the calculation results. The recording speed has been increased, the file size has been significantly reduced.
- Error that occurred when restarting the calculation with the initial temperature fields conditions was fixed.
- Fixed memory access error when calculating on extremely large meshes.
Hooke Stress Solver
- A new module for hot cracks calculating during continuous casting has replaced the traditional GUI model. Now parameters setup and model start is performed from the Start Simulation and Parameters window.
- Module algorithms have been changed and redesigned to work with new material properties format.
- The solver algorithms have been modified and redesigned to calculate stresses in a form that has "empty" volumes.
- Mechanical properties checks ws added . This will avoid situations when inadequate results may be obtained.
- A non-critical bug has been fixed that could lead to an incorrect assessment of the temperature field of the casting before removing it from the mold.
- File names of additional fields have been corrected, now all additional fields are written to files named *_stress_*.u3d.
Heat Treatment Solver
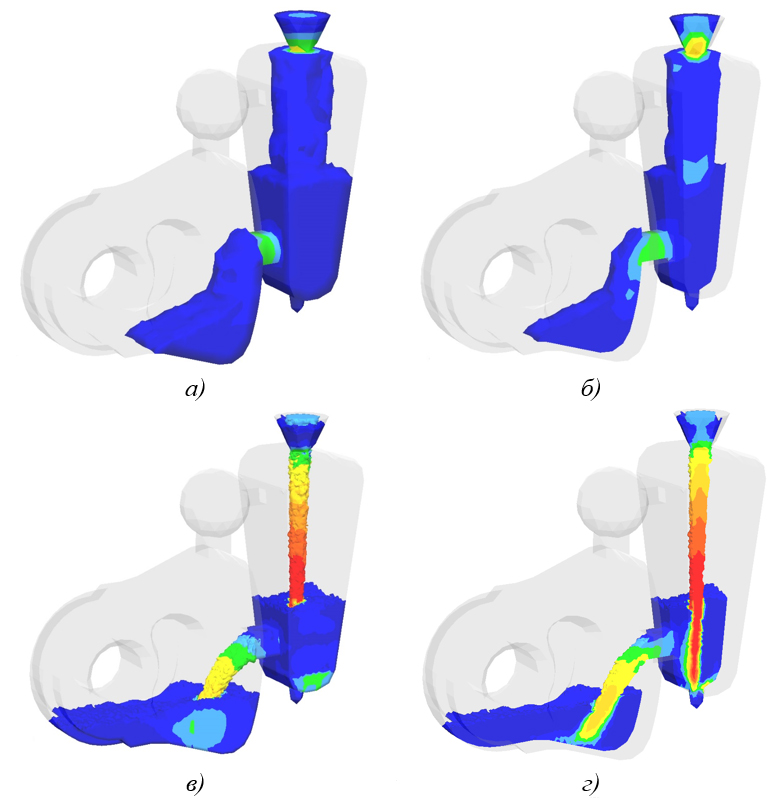
- New solver for calculating the structure and mechanical properties of steel (see figure below).
Simulation of cylinder end hardening: a) martensite; b) bainite;
c) ferrite-pearlite mixture; d) Vickers hardness; e) tensile strength, MPa
- The heat treatment model works together with the Fourier solver.
- The parameters required to run the model are set on the Heat Treatment tab in the Start Simulation and Parameters window.
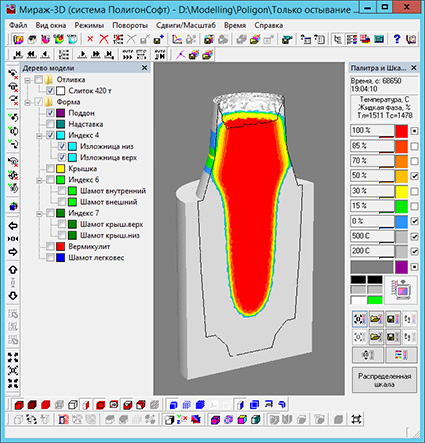
Postprocessor Mirage
- Density field export in Nastran format (NTL file) added. Data in this format can be loaded into other engineering analysis software, such as forging simulation programs.
- Deformed mesh export in STL format added . This can be useful for analyzing the distortion of a part relative to its ideal model in a CAD.
- Error that occurred when loading stress files fixed.
- Other minor improvements in the module.